Understanding Government Cover Letters
Writing a cover letter for a government job requires a strategic approach, distinct from the private sector. Government applications often involve specific requirements and a formal tone. This guide will help you navigate the process, emphasizing how to highlight your qualifications effectively and increase your chances of landing your desired position. A well-crafted cover letter is your opportunity to make a strong first impression, showcasing not only your skills but also your understanding of the agency and the specific role.
Key Differences From Private Sector
Government cover letters frequently emphasize adherence to specific guidelines and requirements outlined in the job announcement. Unlike some private sector applications that might allow for more creativity, government applications are often evaluated based on strict criteria. Government jobs often require detailed documentation of your qualifications, including specific examples that demonstrate your skills. The language used should also be formal and professional, avoiding overly casual language.
Highlighting Relevant Skills and Experience

The primary goal of your cover letter is to connect your skills and experience to the specific requirements of the job. Focus on the keywords and phrases used in the job announcement and ensure you address each requirement in detail. Provide concrete examples, using the STAR method (Situation, Task, Action, Result) to demonstrate how you’ve applied your skills in previous roles. Tailor your letter to each application, ensuring the hiring manager understands why you are a strong fit.
Researching the Specific Job and Agency
Before you start writing, thoroughly research the agency and the specific job you’re applying for. Understand the agency’s mission, values, and recent initiatives. This information will help you tailor your cover letter to show how your skills and experience align with their needs. Visit the agency’s website, read their annual reports, and review any relevant press releases. Demonstrate your genuine interest in the role and the organization.
Structuring Your Government Cover Letter
A well-structured cover letter is essential for making a positive impression. The format of a government cover letter should be clear, concise, and professional. Follow a standard business letter format, ensuring all elements are easy to read. Proper formatting shows your attention to detail and professionalism, which are highly valued in government jobs.
Contact Information and Date

Start with your contact information, including your name, address, phone number, and email address. Include the date below your information, then leave a space and add the hiring manager’s name and title (if you know it), and the agency’s address. This sets a professional tone from the start.
Addressing the Hiring Manager
Always address the hiring manager by name if possible. If you cannot find the name, use a professional salutation like “Dear Hiring Manager.” Avoid generic greetings like “To Whom It May Concern.” Personalizing your salutation shows you’ve done your research and that you’re serious about the position. It is important to research the hiring manager before writing your cover letter.
Opening Paragraph
In the opening paragraph, state the position you’re applying for and where you saw the job posting. Briefly mention your key qualifications and express your enthusiasm for the role and the agency. Clearly state your purpose for writing the letter to immediately grab the reader’s attention. Show you understand the job and agency’s needs, and briefly state how your skills can help fulfill these needs.
Body Paragraphs

Use the body paragraphs to elaborate on your skills and experience, matching them to the job requirements. Refer to the job announcement and address each of the essential and desired qualifications. Use specific examples and the STAR method to demonstrate your accomplishments. Provide evidence of your skills and how you have used them in the past. Quantify your achievements whenever possible, using numbers and data to illustrate your success.
Closing Paragraph
In the closing paragraph, reiterate your interest in the position and express your gratitude for their time and consideration. Provide a call to action, such as stating your availability for an interview. Thank the reader, and include your contact information again, just in case the reader has skipped to the end of the letter.
Formatting and Tone
Maintain a formal and professional tone throughout your cover letter. Use clear, concise language and avoid jargon or slang. Proofread carefully for grammar and spelling errors. The formatting should be clean and easy to read, using a standard font like Times New Roman or Arial, with a font size between 10 and 12 points. Maintain a professional tone and use formal language.
Showcasing Your Qualifications

Effectively showcasing your qualifications is essential to get noticed. Tailor your cover letter to highlight the skills and experiences most relevant to the job requirements. The goal is to demonstrate your value to the hiring manager and persuade them that you are the best candidate for the position.
Analyzing the Job Announcement
Carefully read and analyze the job announcement to understand the specific requirements, qualifications, and responsibilities of the position. Identify the keywords and phrases that are used to describe the desired skills and experiences. Understand the essential qualifications and desired qualifications. Make sure you understand what the agency wants from their ideal candidate.
Matching Skills to Requirements
Create a clear link between your skills and the requirements listed in the job announcement. Give examples of how you have successfully used your skills to achieve results in previous roles. Use the STAR method to provide specific examples of your accomplishments. Demonstrate how your skills align with what the employer is looking for. Mention both technical skills and soft skills that are relevant to the job.
Quantifying Achievements

Whenever possible, quantify your achievements with numbers and data. This provides concrete evidence of your abilities and the impact you’ve made in previous roles. Instead of saying “improved efficiency,” say “improved efficiency by 15%.” Using numbers makes your achievements more credible and memorable, and shows you focus on tangible results. Try to use data to support the claims that you make in your cover letter.
Keywords and Action Verbs
Use keywords from the job announcement throughout your cover letter, as this helps to demonstrate that you meet the qualifications. Use strong action verbs to describe your accomplishments and responsibilities. Action verbs make your writing more dynamic and engaging, making the hiring manager want to know more about you. Use verbs like “managed,” “led,” “achieved,” “developed,” and “implemented” to highlight your accomplishments.
Proofreading and Submission
Before submitting your cover letter, careful proofreading is critical. Errors can undermine your credibility and make a negative impression. Make sure your cover letter is free of typos and grammatical errors. Ensure all your information is accurate. A well-proofread letter shows attention to detail, an important quality in government jobs.
Common Mistakes to Avoid

Avoid these common mistakes to increase your chances of success. Do not use a generic cover letter, and always tailor your application to the specific job. Avoid using slang and informal language. Do not exceed the length requirements stated in the job announcement. Do not focus only on your duties without demonstrating your achievements.
Proofreading Checklist
Use this checklist to ensure your cover letter is polished. Check for grammar and spelling errors. Verify the accuracy of your contact information. Make sure your tone is professional. Confirm your letter matches the job requirements. Have someone else review your letter. Ensure the formatting is correct. Double check that you have included all required attachments.
Submitting Your Application
Carefully follow the instructions provided in the job announcement for submitting your application. Make sure you submit all required documents, such as your resume, cover letter, and any supplemental forms. Check the submission deadline and submit your application before the deadline. If you have any technical difficulties, contact the agency immediately for assistance.
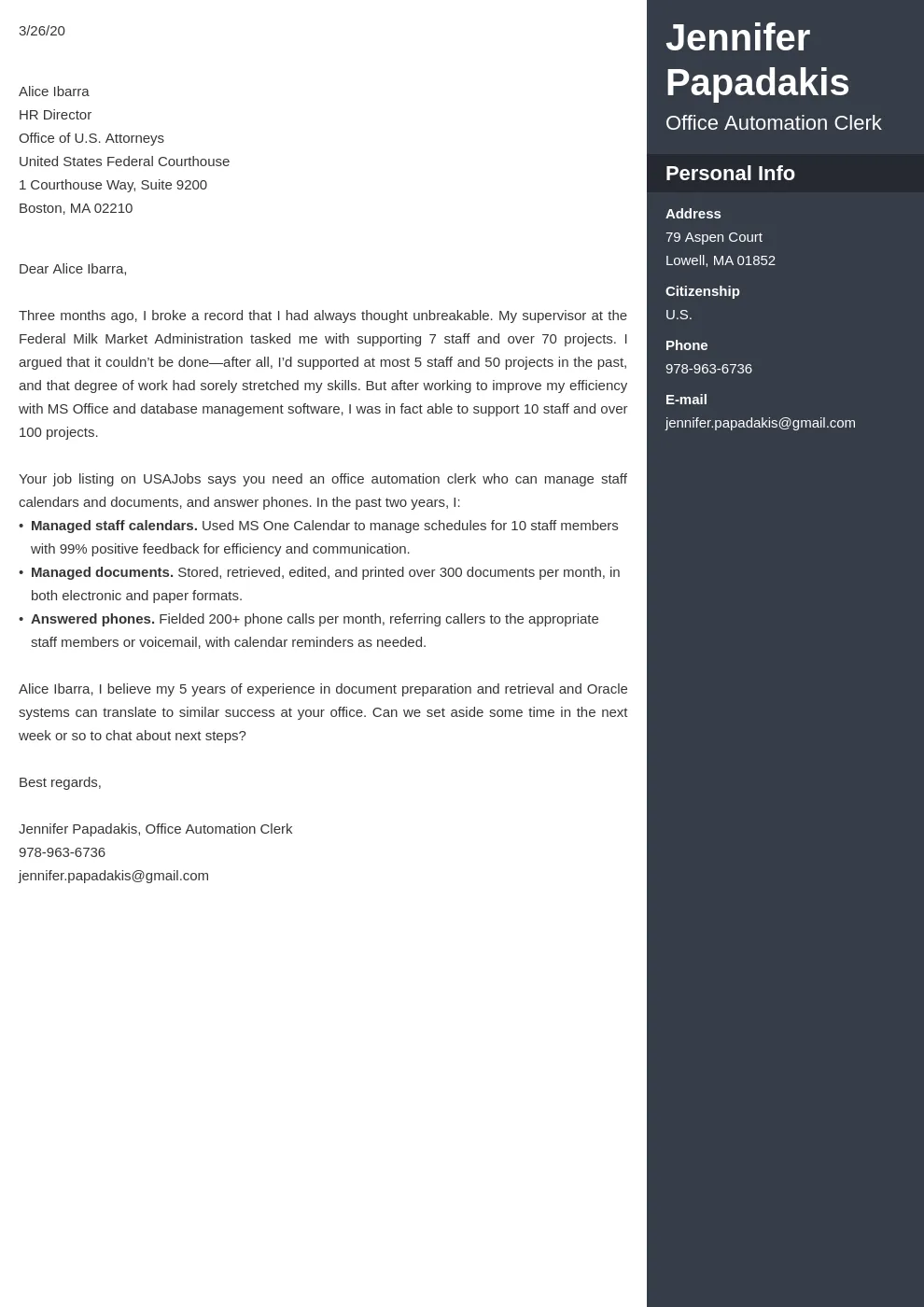
Example Cover Letter
Here’s an example of how to format your cover letter, including the essential elements mentioned above. Note this is a template and you must fill in with your information and tailor it to the specific job.
Example Paragraphs for Different Skills
Here’s some examples of how to articulate your skills and experience. For example, if the job requires project management, show off your project management abilities. If the job requires communication skills, describe specific instances where you’ve effectively communicated complex information. Tailor each paragraph to emphasize the skills most relevant to the specific job requirements.
By following these guidelines, you’ll be well on your way to writing a compelling cover letter and securing a government job. Good luck!